Spring事件驱动过程分析
在看Spring源码之前确保理解了JDK中的 EventObject,EventListener的使用场景,其实体现的是观察者模式,适用于很多场景。
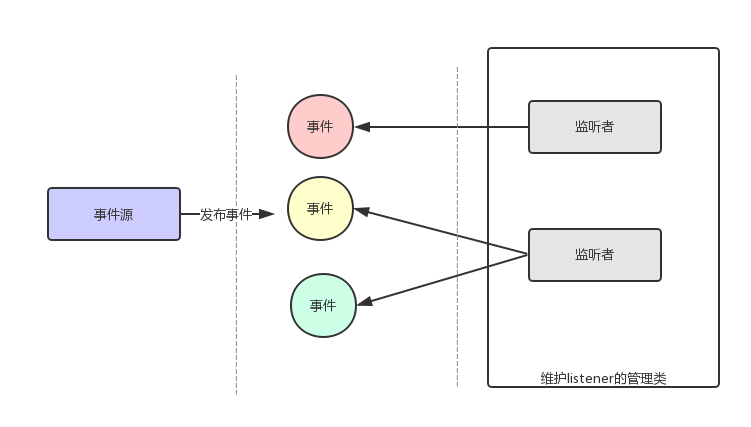
在Spring中,事件基类ApplicationEvent,在应用的周期中触发(发布)相应的事件。
public abstract class ApplicationEvent extends EventObject {
/** use serialVersionUID from Spring 1.2 for interoperability */
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7099057708183571937L;
/** System time when the event happened */
private final long timestamp;
/**
* Create a new ApplicationEvent.
* @param source the object on which the event initially occurred (never {@code null})
*/
public ApplicationEvent(Object source) {
super(source);
this.timestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
/**
* Return the system time in milliseconds when the event happened.
*/
public final long getTimestamp() {
return this.timestamp;
}
}
监听器基类如下,在接收到事件后如果是自己感兴趣的就进行相应处理。
public interface ApplicationListener<E extends ApplicationEvent> extends EventListener {
/**
* Handle an application event.
* @param event the event to respond to
*/
void onApplicationEvent(E event);
}
Spring boot在启动的时候会加载一部分 ApplicationListener。Spring Context加载初始化完成(refresh)后会再次检测应用中的 ApplicationListener,并且注册,此时会将我们实现的 ApplicationListener 就会加入到 SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster 维护的 Listener 集合中。
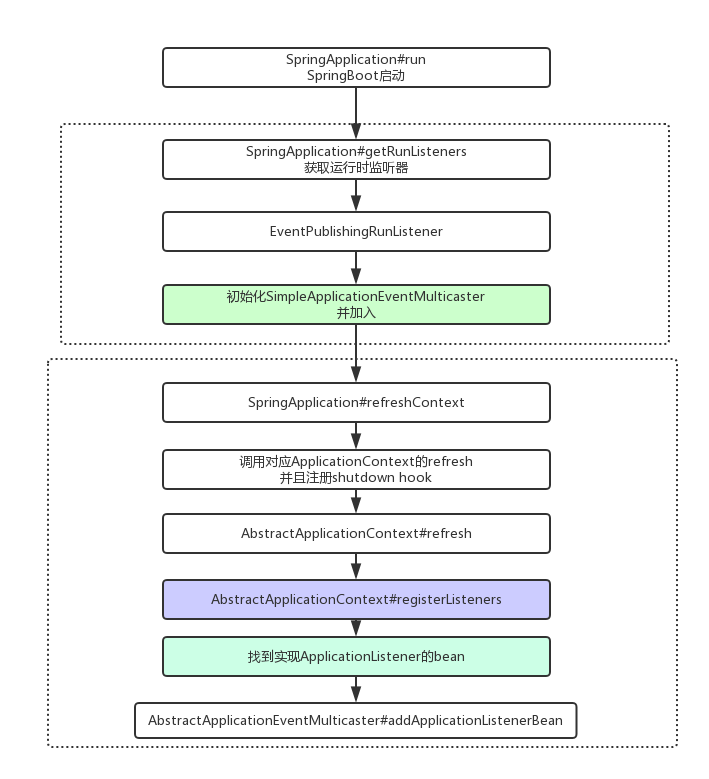 事件触发的流程是怎样的?以 ContextRefreshedEvent 为例。在Context初始化完成后,在 finishRefresh 方法中会发布 ContextRefreshedEvent 事件。
事件触发的流程是怎样的?以 ContextRefreshedEvent 为例。在Context初始化完成后,在 finishRefresh 方法中会发布 ContextRefreshedEvent 事件。
protected void finishRefresh() {
// Initialize lifecycle processor for this context.
initLifecycleProcessor();
// Propagate refresh to lifecycle processor first.
getLifecycleProcessor().onRefresh();
// Publish the final event.
publishEvent(new ContextRefreshedEvent(this));
// Participate in LiveBeansView MBean, if active.
LiveBeansView.registerApplicationContext(this);
}
protected void publishEvent(Object event, ResolvableType eventType) {
// Decorate event as an ApplicationEvent if necessary
ApplicationEvent applicationEvent;
if (event instanceof ApplicationEvent) {
applicationEvent = (ApplicationEvent) event;
}
else {
applicationEvent = new PayloadApplicationEvent<Object>(this, event);
if (eventType == null) {
eventType = ((PayloadApplicationEvent)applicationEvent).getResolvableType();
}
}
// Multicast right now if possible - or lazily once the multicaster is initialized
if (this.earlyApplicationEvents != null) {
this.earlyApplicationEvents.add(applicationEvent);
}
else { // 多播事件
getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(applicationEvent, eventType);
}
// Publish event via parent context as well... 上层的Context也会响应该事件
if (this.parent != null) {
if (this.parent instanceof AbstractApplicationContext) {
((AbstractApplicationContext) this.parent).publishEvent(event, eventType);
}
else {
this.parent.publishEvent(event);
}
}
}
public void multicastEvent(final ApplicationEvent event, ResolvableType eventType) {
ResolvableType type = (eventType != null ? eventType : resolveDefaultEventType(event));
for (final ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners(event, type)) {
Executor executor = getTaskExecutor();
// 如果设置了 Executor 则异步执行
if (executor != null) {
executor.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
invokeListener(listener, event);
}
});
}
else {// 否则同步调用listener的事件处理方法
invokeListener(listener, event);
}
}
}
内部 listener 是如何维护的?使用的哪种集合?是否线程安全?
org.springframework.context.event.AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster.ListenerRetriever
private class ListenerRetriever {
// 这里
public final Set<ApplicationListener<?>> applicationListeners;
public final Set<String> applicationListenerBeans;
private final boolean preFiltered;
public ListenerRetriever(boolean preFiltered) {
this.applicationListeners = new LinkedHashSet<ApplicationListener<?>>();
this.applicationListenerBeans = new LinkedHashSet<String>();
this.preFiltered = preFiltered;
}
public Collection<ApplicationListener<?>> getApplicationListeners() {
LinkedList<ApplicationListener<?>> allListeners = new LinkedList<ApplicationListener<?>>();
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : this.applicationListeners) {
allListeners.add(listener);
}
if (!this.applicationListenerBeans.isEmpty()) {
BeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
for (String listenerBeanName : this.applicationListenerBeans) {
try {
ApplicationListener<?> listener = beanFactory.getBean(listenerBeanName, ApplicationListener.class);
if (this.preFiltered || !allListeners.contains(listener)) {
allListeners.add(listener);
}
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// Singleton listener instance (without backing bean definition) disappeared -
// probably in the middle of the destruction phase
}
}
}
// 根据Order注解排序
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(allListeners);
return allListeners;
}
}
在增加元素到Set的时候有同步操作。
// 使用 ListenerRetriever 作为加锁对象
private Object retrievalMutex = this.defaultRetriever;
public void addApplicationListener(ApplicationListener<?> listener) {
synchronized (this.retrievalMutex) {
this.defaultRetriever.applicationListeners.add(listener);
this.retrieverCache.clear();
}
}
public void addApplicationListenerBean(String listenerBeanName) {
synchronized (this.retrievalMutex) {
this.defaultRetriever.applicationListenerBeans.add(listenerBeanName);
this.retrieverCache.clear();
}
}
本文由 创作,采用 知识共享署名4.0 国际许可协议进行许可。本站文章除注明转载/出处外,均为本站原创或翻译,转载前请务必署名。最后编辑时间为: 2020/11/28 03:46
