Android 串口通讯设置校验位、速率、停止位等参数(初版,有BUG)
最近业余时间有个android项目需要和硬件进行通信,通讯方式都是通过串口,android串口通讯google有个开源的demo 和很多人一样我也是通过下载这个demo进行开发和研究的。
google android串口通讯开源demo地址:https://code.google.com/archive/p/android-serialport-api/
串口通讯中我们可能会要设置校验位、速率、停止位等参数,但一般情况下还是不用设置的,只需要设置波特率就行。google提供的demo中就只提供一个波特率的设置其他的参数一并没有提供。
在使用google 源码的时候一定要注意 jni 当中.h和.c文件中的方法命名的规则,是java关键字+包名+类名+方法名。一开始我没注意,程序报错走了好多弯路。所以画图具体解释下。
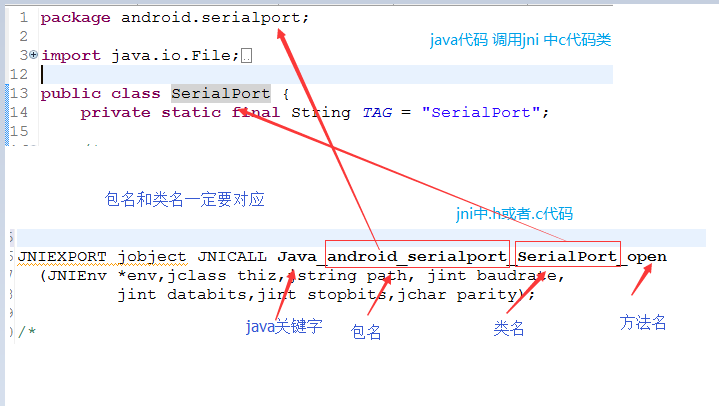
android串口通讯说到底其实还是linux串口通讯。我们jni中的c代码其实就是操作linux中提供的串口文件。一开始并不知道这个原理,只是后来在网上找如何设置校验位、速率等问题时才明白的。
比如打开串口 fd = open("/dev/ttyS0", O_RDWR | O_NOCTTY | O_NDELAY);其实就是打开linux设备中串口文件。串口文件都是以ttys开头 如ttys0 等。这个fd很重要,应该就是代表当前串口文件对象。只要这里打开成功了,C代码其他地方对串口的操作以及配置都是基于这个fd来进行的。
在adb 中可以用 cd dev来查看是否有串口文件。如果看到了 ttys0等这样的文件说明目前设备上有串口否则没有找到串口设备。
adb 中通过命令向串口发送数据:echo -e "AT\r\n">/dev/ttyS0
顺便说下如何在模拟器中使用电脑上的串口 这个只能使用android自带的模拟器。 一直想如果第三方模拟器能加载电脑的串口设备就好了。
emulator @模拟器名称 -qemu -serial COM1 // 这个命令会自动启动安卓模拟器
chmod 777 ttyS2 //提示权限 串口设备文件 ttys2
废话不多说,下面附上完整的代码。
注:代码是google的源代码+网上找的一些参考资料=现在的一个整合代码。
注意C和h代码中的数据类型,尽量以jint、jstring等来定义。(jint相当于java的int...)因为要被java调用,所以做好这样定义: .h代码(用于jni方法声明 即要在java中调用的方法声明)注意包名+类名+方法名
SerialPort.h
/* DO NOT EDIT THIS FILE - it is machine generated */
#include <jni.h>
/* Header for class org_winplus_serial_utils_SerialPort */
#ifndef _Included_android_serialport_SerialPort
#define _Included_android_serialport_SerialPort
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C" {
#endif
/*
* Class: org_winplus_serial_utils_SerialPort
* Method: open
* Signature: (Ljava/lang/String;II)Ljava/io/FileDescriptor;
*/
JNIEXPORT jobject JNICALL Java_android_serialport_SerialPort_open
(JNIEnv *env, jclass thiz, jstring path, jint baudrate,
jint databits, jint stopbits, jchar parity);
/*
* Class: org_winplus_serial_utils_SerialPort
* Method: close
* Signature: ()V
*/
JNIEXPORT void JNICALL Java_android_serialport_SerialPort_close
(JNIEnv *, jobject);
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
#endif
.C代码(用于jni方法的具体实现代码本例中串口操作的所有代码)注意包名+类名+方法名
注意C代码中 写一个方法,一定要写到调用地方的前面。或者前面写声明;即 A要调用B方法,B方法代码必须要在A方法前面。由于平时写java或者c#这些代码是不需要这样的写法。一时切换到C代码可能容易忘记。
SerialPort.C
#include <termios.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <jni.h>
#include "SerialPort.h"
#include "android/log.h"
static const char *TAG = "serial_port";
#define LOGI(fmt, args...) __android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_INFO, TAG, fmt, ##args)
#define LOGD(fmt, args...) __android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_DEBUG, TAG, fmt, ##args)
#define LOGE(fmt, args...) __android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_ERROR, TAG, fmt, ##args)
int fd;
static speed_t getBaudrate(jint baudrate)
{
switch(baudrate)
{
case 0:
return B0;
case 50:
return B50;
case 75:
return B75;
case 110:
return B110;
case 134:
return B134;
case 150:
return B150;
case 200:
return B200;
case 300:
return B300;
case 600:
return B600;
case 1200:
return B1200;
case 1800:
return B1800;
case 2400:
return B2400;
case 4800:
return B4800;
case 9600:
return B9600;
case 19200:
return B19200;
case 38400:
return B38400;
case 57600:
return B57600;
case 115200:
return B115200;
case 230400:
return B230400;
case 460800:
return B460800;
case 500000:
return B500000;
case 576000:
return B576000;
case 921600:
return B921600;
case 1000000:
return B1000000;
case 1152000:
return B1152000;
case 1500000:
return B1500000;
case 2000000:
return B2000000;
case 2500000:
return B2500000;
case 3000000:
return B3000000;
case 3500000:
return B3500000;
case 4000000:
return B4000000;
default:
return -1;
}
}
/**
* 设置串口数据,校验位,速率,停止位
* @param nBits 类型 int数据位 取值 位7或8
* @param nEvent 类型 char 校验类型 取值N ,E, O,,S
* @param mStop 类型 int 停止位 取值1 或者 2
*/
int set_opt(jint nBits, jchar nEvent, jint nStop){
LOGE("set_opt:nBits=%d,nEvent=%c,nSpeed=%d,nStop=%d", nBits, nEvent, nStop);
struct termios newtio;
if(tcgetattr(fd, & newtio) != 0) {
LOGE("setup serial failure");
return -1;
}
bzero( &newtio, sizeof(newtio));
//c_cflag标志可以定义CLOCAL和CREAD,这将确保该程序不被其他端口控制和信号干扰,同时串口驱动将读取进入的数据。CLOCAL和CREAD通常总是被是能的
newtio.c_cflag |= CLOCAL | CREAD;
//设置数据位数
switch(nBits) {
case 7:
newtio.c_cflag &= ~CSIZE;
newtio.c_cflag |= CS7;
break;
case 8:
newtio.c_cflag &= ~CSIZE;
newtio.c_cflag |= CS8;
break;
default:
break;
}
//设置校验位
switch(nEvent){
case 'O':
newtio.c_cflag |= PARENB; //enable parity checking
newtio.c_cflag |= PARODD; //奇校验位
newtio.c_iflag |= (INPCK | ISTRIP);
break;
case 'E':
newtio.c_cflag |= PARENB; //
newtio.c_cflag &= ~PARODD; //偶校验位
newtio.c_iflag |= (INPCK | ISTRIP);
break;
case 'N':
newtio.c_cflag &= ~PARENB; //清除校验位
break;
default:
break;
}
//设置停止位
switch(nStop) {
case 1:
newtio.c_cflag &= ~CSTOPB;
break;
case 2:
newtio.c_cflag |= CSTOPB;
break;
default:
// LOGW("nStop:%d,invalid param", nStop);
break;
}
newtio.c_cc[VTIME] = 0;//设置等待时间
newtio.c_cc[VMIN] = 0;//设置最小接收字符
tcflush(fd, TCIFLUSH);
if(tcsetattr(fd, TCSANOW, & newtio) != 0){
LOGE("options set error");
return -1;
}
LOGE("options set success");
return 1;
}
/*
* Class: android_serialport_SerialPort
* Method: open
* Signature: (Ljava/lang/String;II)Ljava/io/FileDescriptor;
*/
JNIEXPORT jobject JNICALL Java_android_serialport_SerialPort_open
(JNIEnv *env, jclass thiz, jstring path, jint baudrate,
jint databits, jint stopbits, jchar parity) {
speed_t speed;
jobject mFileDescriptor;
/*波特率 */
{
speed = getBaudrate(baudrate);
if (speed == -1) {
/* TODO: throw an exception */
LOGE("Invalid baudrate");
return NULL;
}
}
/* Opening device */
{
jint flags = 0;
jboolean iscopy;
const char *path_utf = (*env)->GetStringUTFChars(env, path, &iscopy);
LOGD("Opening serial port %s with flags 0x%x", path_utf, O_RDWR | flags);
fd = open(path_utf, O_RDWR | O_NONBLOCK);
//fd=fd;
LOGD("open() fd = %d", fd);
(*env)->ReleaseStringUTFChars(env, path, path_utf);
if (fd == -1) {
/* Throw an exception */
LOGE("Cannot open port");
/* TODO: throw an exception */
return NULL;
}
}
/* Configure device */
{
struct termios cfg;
LOGD("Configuring serial port");
if (tcgetattr(fd, &cfg)) {
LOGE("tcgetattr() failed");
close(fd);
/* TODO: throw an exception */
return NULL;
}
cfmakeraw(&cfg);
//设置波特率
cfsetispeed(&cfg, speed);
cfsetospeed(&cfg, speed);
if (tcsetattr(fd, TCSANOW, &cfg)) {
LOGE("tcsetattr() failed");
close(fd);
/* TODO: throw an exception */
return NULL;
}
//配置校验位 停止位等等
set_opt(databits, parity, stopbits);
}
/* Create a corresponding file descriptor */
{
jclass cFileDescriptor = (*env)->FindClass(env, "java/io/FileDescriptor");
jmethodID iFileDescriptor = (*env)->GetMethodID(env, cFileDescriptor, "<init>", "()V");
jfieldID descriptorID = (*env)->GetFieldID(env, cFileDescriptor, "descriptor", "I");
mFileDescriptor = (*env)->NewObject(env, cFileDescriptor, iFileDescriptor);
(*env)->SetIntField(env, mFileDescriptor, descriptorID, (jint)fd);
}
return mFileDescriptor;
}
/*
* Class: cedric_serial_SerialPort
* Method: close
* Signature: ()V
*/
JNIEXPORT void JNICALL Java_android_serialport_SerialPort_close
(JNIEnv *env, jobject thiz) {
jclass SerialPortClass = (*env)->GetObjectClass(env, thiz);
jclass FileDescriptorClass = (*env)->FindClass(env, "java/io/FileDescriptor");
jfieldID mFdID = (*env)->GetFieldID(env, SerialPortClass, "mFd", "Ljava/io/FileDescriptor;");
jfieldID descriptorID = (*env)->GetFieldID(env, FileDescriptorClass, "descriptor", "I");
jobject mFd = (*env)->GetObjectField(env, thiz, mFdID);
jint descriptor = (*env)->GetIntField(env, mFd, descriptorID);
LOGD("close(fd = %d)", descriptor);
close(descriptor);
}
java代码 调用jni提供的方法进行串口操作
package android.serialport;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileDescriptor;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import android.util.Log;
public class SerialPort {
private static final String TAG = "SerialPort";
private FileDescriptor mFd;
private FileInputStream mFileInputStream;
private FileOutputStream mFileOutputStream;
/***
* 构造方法
* @param device 串口文件
* @param baudrate 波特率
* @param dataBits 数据位
* @param stopBits 停止位
* @param parity 校验位
* @throws SecurityException
* @throws IOException
*/
public SerialPort(File device, int baudrate, int dataBits,int stopBits,char parity)
throws SecurityException, IOException {
/* Check access permission */
if (!device.canRead() || !device.canWrite()) {
try {
/* Missing read/write permission, trying to chmod the file */
Process su;
su = Runtime.getRuntime().exec("/system/bin/su");
String cmd = "chmod 666 " + device.getAbsolutePath() + "\n"
+ "exit\n";
su.getOutputStream().write(cmd.getBytes());
if ((su.waitFor() != 0) || !device.canRead()
|| !device.canWrite()) {
throw new SecurityException();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new SecurityException();
}
}
mFd = open(device.getAbsolutePath(), baudrate, dataBits,stopBits,parity);
if (mFd == null) {
Log.e(TAG, "native open returns null");
throw new IOException();
}
mFileInputStream = new FileInputStream(mFd);
mFileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(mFd);
}
// Getters and setters
public InputStream getInputStream() {
return mFileInputStream;
}
public OutputStream getOutputStream() {
return mFileOutputStream;
}
// 调用JNI中 打开方法的声明
private native static FileDescriptor open(String path, int baudrate,
int dataBits,int stopBits,char parity);
public native void close();
static {
System.loadLibrary("serial_port");
}
}
本文由 创作,采用 知识共享署名4.0 国际许可协议进行许可。本站文章除注明转载/出处外,均为本站原创或翻译,转载前请务必署名。最后编辑时间为: 2020/09/11 01:53
