算法:两种对拼音进行智能切分的方法
前言
最近在做一个调研的工作。研究的对象是搜索引擎中关键词的纠错功能。就像百度中搜索某一个关键词“ABC”,它会在搜索的结果中对此关键词进行纠正,然后会显示:你要找的是不是“ABD”。这种之类的。这个是背景,不过本文中还没不是介绍这一功能,这一功能的说明会在我的调研结束之后写在我的博客中。
本文要介绍的是,对拼音的拼写进行智能切分。比如:qinshimingyuezhijunlintianxia这一串拼音字符串,我们要如何对其进行切分呢?本文将要用两种方法介绍这个汉语拼音的智能切分功能。
1. 字典树算法
关于字典树(Trie tree),大家可以从下面的展示图中看出。
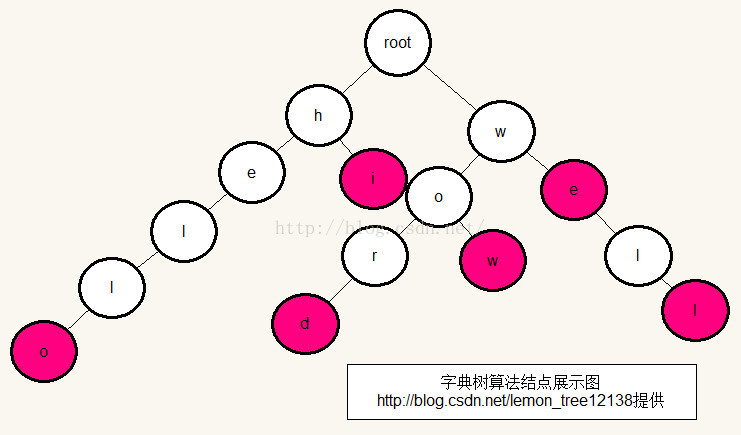
(1)基本算法的实现
这里我想先就这个算法做一个基本的实现,再在这个基础上做拼音的智能切分。毕竟路是一步一步走出来的,不必要急于求成,这也是在软件开发过程中一个很关键的地方。
我们使用面向对象的编程语言Java来编写代码。在图中可以看出,每个节点即是一个对象。这个对象有以下一些属性:节点名称信息/词频/是否是单词的结尾字母/是否是root节点/孩子节点。而对于整个一棵树又是另外的一个对象。于是,我们可以编写出如下的代码:
节点对象:
public class Node {
String name; // 结点的字符名称
int fre; // 单词的词频
boolean end; // 是否是单词结尾
boolean root; // 是否是根结点
Map<String, Node> childrens; // 子节点信息
public Node(String name) {
this.name = name;
if (childrens == null) {
childrens = new HashMap<String, Node>();
}
setFre(0);
setRoot(false);
setEnd(false);
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getFre() {
return fre;
}
public void setFre(int fre) {
this.fre = fre;
}
public boolean isEnd() {
return end;
}
public void setEnd(boolean end) {
this.end = end;
}
public boolean isRoot() {
return root;
}
public void setRoot(boolean root) {
this.root = root;
}
public Map<String, Node> getChildrens() {
return childrens;
}
public void setChildrens(Map<String, Node> childrens) {
this.childrens = childrens;
}
}
字典树对象:
public class TrieTree {
Node root;
public TrieTree(String name) {
root = new Node(name);
root.setFre(0);
root.setEnd(false);
root.setRoot(true);
}
public void insert(String word) {
// ...
}
public int searchFre(String word) {
// ...
}
}
测试代码:
public class TireTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TrieTree tree = new TrieTree("test");
tree.insert("word");
tree.insert("word");
tree.insert("hello");
tree.insert("hi");
System.out.println("word " + tree.searchFre("word"));
System.out.println("hello " + tree.searchFre("hello"));
System.out.println("hi " + tree.searchFre("hi"));
System.out.println("hell " + tree.searchFre("hell"));
System.out.println("hellt " + tree.searchFre("hellt")); // qinshimingyuezhijunlintianxia
}
}
测试结果:
word 2
hello 1
hi 1
hell 0
hellt -1
在上面的字典树对象的代码中,我把两个最关键方法给略去了,这里我给补上,目的只是强调这两个方法的关键性,别无他意。
插入:
对于插入单词操作。因为单词的长度是已知的,所以,这里我们就可以以单词长度作为限制进行循环。在插入单词的过程中,如果某一个字母已经存在,则将遍历的位置移至此节点,如果发现某一个字母不存在,则新建一个,再移动遍历节点。
public void insert(String word) {
Node node = root;
char[] words = word.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < words.length; i++) {
if (node.getChildrens().containsKey(words[i] + "")) {
if (i == words.length - 1) {
Node endNode = node.getChildrens().get(words[i] + "");
endNode.setFre(endNode.getFre() + 1);
endNode.setEnd(true);
}
} else {
Node newNode = new Node(words[i] + "");
if (i == words.length - 1) {
newNode.setFre(1);
newNode.setEnd(true);
newNode.setRoot(false);
}
node.getChildrens().put(words[i] + "", newNode);
}
node = node.getChildrens().get(words[i] + "");
}
}
查找:
对于查找,相对于插入代码量要小一些。这是因为在查找的过程中,如果找到了就继续直到单词结尾,如果没找到就返回,很干脆。
public int searchFre(String word) {
int fre = -1;
Node node = root;
char[] words = word.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < words.length; i++) {
if (node.getChildrens().containsKey(words[i] + "")) {
node = node.getChildrens().get(words[i] + "");
fre = node.getFre();
} else {
fre = -1;
break;
}
}
return fre;
}
(2)拼音智能切分
对于拼音智能切分,我们就利用了上面的字典。如果你认真看了上面的说明和代码实践或是你已经了解了字典树,那么我想关于这里的拼音切分就更加难不倒你了。因为在上面代码的基础上,我们只做一点点的修改,就可以完成我们理想拼音智能切分了。如下:
public String splitSpell(String spell) {
Node node = root;
char[] letters = spell.toCharArray();
String spells = "";
for (int i = 0; i < letters.length; i++) {
if (node.getChildrens().containsKey(letters[i] + "")) {
spells += letters[i];
node = node.getChildrens().get(letters[i] + "");
} else {
node = root;
spells += " ";
i--;
}
}
return spells;
}
结果:
对拼音串qinshimingyuezhijunlintianxia的切分结果如下:
qin shi ming yue zhi jun lin tian xia
2.正则匹配
关于正则的匹配,这里就不作过多的说明。代码如下:
public static String splitSpell(String s) {
String regEx = "[^aoeiuv]?h?[iuv]?(ai|ei|ao|ou|er|ang?|eng?|ong|a|o|e|i|u|ng|n)?";
int tag = 0;
String spell = "";
List<String> tokenResult = new LinkedList<String>();
for (int i = s.length(); i > 0; i = i - tag) {
Pattern pat = Pattern.compile(regEx);
Matcher matcher = pat.matcher(s);
matcher.find();
spell += (matcher.group() + " ");
tag = matcher.end() - matcher.start();
tokenResult.add(s.substring(0, 1));
s = s.substring(tag);
}
return spell;
}
源码下载:
代码为完整源码,包含完整的代码实现和完整的拼音表
- http://download.csdn.net/detail/u013761665/9175663
- http://www.yanzuoguang.com/upload/2020/06/vmtdg6mtrqjvhpjbna89bb3sdi.zip
本文由 创作,采用 知识共享署名4.0 国际许可协议进行许可。本站文章除注明转载/出处外,均为本站原创或翻译,转载前请务必署名。最后编辑时间为: 2020/06/29 13:03
