浅谈Vue组件传参(常见的几种通信方式)
Vue的通信方式,也可以说是传参方式。主要分为四种:
- 父子传参
- 子父传参
- 相邻兄弟传参(亲兄弟)
- 远兄弟传参(表兄弟)
一、父子传参
原理:父控制子,通过子组件的props属性,抛出子组件自定义标签属性,来接收父组件的操作状态
例子:父级里的一个按钮,控制子组件里的一个div的显示隐藏
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<style>
.div{
width:200px;
height:200px;
background:pink;
}
</style>
<body>
<!-- 这里的app范围就是 子组件son 的父级 -->
<div id="app">
<button @click='change'>父按钮</button>
<hr>
<!-- ********** 自定义标签属性test,接收父级的state ************-->
<son :test='state'></son>
</div>
<template id="tp1">
<div>
<!-- ************ 调用自定义属性test **************-->
<div class="div" v-show='test'>我是子组件的div</div>
</div>
</template>
<script src="../vue/vue.js"></script>
<script>
// 局部定义 子组件son
new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
state:true
},
methods:{
change(){
this.state = !this.state;
}
},
components:{
son:{
template:"#tp1",
//*********** 抛出自定义标签属性 ***************
props:['test']
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
效果:

二、子父传参
原理:子控制父,子组件绑定自定义事件,来处理父组件的方法函数,通过.$emit(‘自定义事件’,[参数])来触发属于自己的自定义事件
例子:子组件里一个按钮,控制父组件里的一个div的显示隐藏
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<style>
.div{
width:200px;
height:200px;
background:pink;
}
</style>
<body>
<div id="app">
<c1></c1>
</div>
<!-- 父组件c1 子组件c2 子组件自定义事件test-->
<template id="c1">
<div>
<div class="div" v-show='state'>father显示/隐藏</div>
<hr>
<!--************ 子组件c2自定义事件,执行父组件c1的方法函数change_f ***************** -->
<c2 @test='change_f'></c2>
</div>
</template>
<template id="c2">
<div>
<button @click='change_son'>子按钮</button>
</div>
</template>
<!-- 引入Vue.js框架文档,可在官方文档下载-->
<script src='../vue/vue.js'></script>
<script>
//全局定义
// 实例化 父组件c1
Vue.component("c1",{
template:"#c1",
data(){
return {
state:true
}
},
methods:{
change_f(){
this.state = !this.state;
}
}
});
// 实例化 子组件c2
Vue.component("c2",{
template:"#c2",
methods:{
change_son(){
// ************ 在子组件方法里,触发子组件自定义事件 ******************
this.$emit("test")
}
}
})
//实例化一个Vue对象
new Vue({
el:"#app"
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
效果:

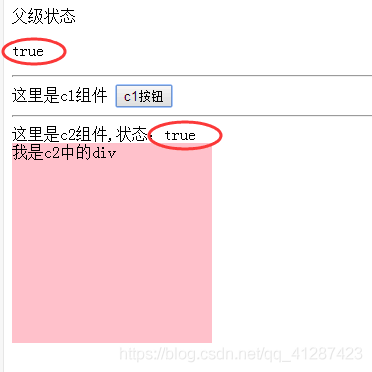
三、相邻兄弟传参(亲兄弟)
原理:通过一个公有的父元素作为桥接(实例 组件),结合父子props 传参 、子父自定义事件
例子:c1、c2是兄弟关系 c1可用控制c2里元素的显示隐藏
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<style>
.div{
width:200px;
height:200px;
background:pink;
}
</style>
<body>
<div id="app">
父级状态
<p>{{state}}</p>
<hr>
<c1 @test_c1='change_f'></c1>
<hr>
<c2 :test_c2='state'></c2>
</div>
<template id="c1">
<div>这里是c1组件
<button @click='change_c1'>c1按钮</button>
</div>
</template>
<template id="c2">
<div>这里是c2组件,状态:{{test_c2}}
<div class="div" v-show='test_c2'>我是c2中的div</div>
</div>
</template>
<script src='../vue/vue.js'></script>
<script>
Vue.component("c2",{
template:"#c2",
props:['test_c2']
})
Vue.component("c1",{
template:"#c1",
methods:{
change_c1(){
this.$emit("test_c1")
}
}
})
new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
state:true
},
methods:{
change_f(){
this.state = !this.state;
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
效果:
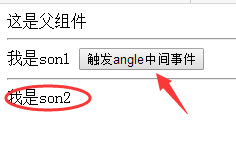
四、远兄弟传参(表兄弟)
原理:通过创建一个中间实例,注册一个事件,在被控组件中,通过事件携带要执行的函数,在主控组件中,通过事件,改变相应的操作
例子:son1组件触发按钮来改变son2组件中name的内容,创建angel实例:let angel = new Vue(),注册test事件:angel.on(′test′ , fun ) , 主控组件操作 : angel.on('test',fun),主控组件操作:angel.on(′test ′ ,fun),主控组件操作:angel.emit('test' , '参数')
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<father></father>
</div>
<template id="father">
<div>
这是父组件
<hr>
<son1></son1>
<hr>
<son2></son2>
</div>
</template>
<template id="son1">
<div>
{{name}}
<button @click='click_son1'>触发angle中间事件</button>
</div>
</template>
<template id="son2">
<div>
{{name}}
</div>
</template>
<script src='../vue/vue.js'></script>
<script>
//********** 创建一个angle实例,作为中间变量(全局) **************
let angel = new Vue();
new Vue({
el:"#app",
components:{
father:{
template:"#father",
components:{
son1:{
template:"#son1",
data(){
return {
name:"我是son1"
}
},
methods:{
click_son1(){
// *************** 通过angel注册的test事件,修改son2中name的值 ************
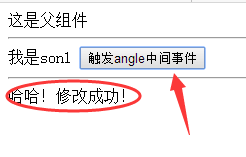
angel.$emit('test','哈哈!修改成功!')
}
}
},
son2:{
template:"#son2",
data(){
return {
name:"我是son2"
}
},
methods:{
change(val){
this.name = val;
}
},
//生命周期,自动执行,组件准备ok就可用
mounted(){
// *************** 通过angel注册的test事件,将son1的修改方法传过去 ************
angel.$on('test',this.change)
}
}
}
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
效果:
点击前:
 点击后:
点击后:
本文由 创作,采用 知识共享署名4.0 国际许可协议进行许可。本站文章除注明转载/出处外,均为本站原创或翻译,转载前请务必署名。最后编辑时间为: 2021/12/31 08:13
