Feign源码解析之自定义配置和注意点
前文
- Feign源码解析之注入IOC容器
- Feign源码解析之生成jdk动态代理
- Feign源码解析之代理类的处理逻辑
- Feign源码解析之使用Hystrix 前面几篇文章都是针对的默认配置进行分析,这一篇文章我们将着重分析Feign的自定义配置,常见的主要有以下几种方式。
一. 对feign属性的覆盖
主要可以覆盖的属性及其默认值如下:
//feign拦截器
private final List<RequestInterceptor> requestInterceptors =
new ArrayList<RequestInterceptor>();
//日志级别
private Logger.Level logLevel = Logger.Level.NONE;
//对方法和接口上的注解进行解析
private Contract contract = new Contract.Default();
//Http客户端接口,默认为Client.Default,也可以是OkHttp,ApacheHttpClient
private Client client = new Client.Default(null, null);
//失败重试
private Retryer retryer = new Retryer.Default();
//日志
private Logger logger = new NoOpLogger();
//编码,由feign方法数据到请求数据
private Encoder encoder = new Encoder.Default();
//解码,由请求响应到feign方法返回值
private Decoder decoder = new Decoder.Default();
//错误时的解码,请求返回错误时的处理
private ErrorDecoder errorDecoder = new ErrorDecoder.Default();
//请求相关的设置,如connectTimeoutMillis连接超时和readTimeoutMillis读超时
private Options options = new Options();
//请求返回404时是否进行编码
private boolean decode404;
protected Feign.Builder feign(FeignContext context) {
FeignLoggerFactory loggerFactory = get(context, FeignLoggerFactory.class);
Logger logger = loggerFactory.create(this.type);
// @formatter:off
Feign.Builder builder = get(context, Feign.Builder.class)
// required values
.logger(logger)
.encoder(get(context, Encoder.class))
.decoder(get(context, Decoder.class))
.contract(get(context, Contract.class));
// @formatter:on
configureFeign(context, builder);
return builder;
}
protected void configureFeign(FeignContext context, Feign.Builder builder) {
FeignClientProperties properties = applicationContext.getBean(FeignClientProperties.class);
if (properties != null) {
if (properties.isDefaultToProperties()) {
configureUsingConfiguration(context, builder);
configureUsingProperties(properties.getConfig().get(properties.getDefaultConfig()), builder);
configureUsingProperties(properties.getConfig().get(this.name), builder);
} else {
configureUsingProperties(properties.getConfig().get(properties.getDefaultConfig()), builder);
configureUsingProperties(properties.getConfig().get(this.name), builder);
configureUsingConfiguration(context, builder);
}
} else {
configureUsingConfiguration(context, builder);
}
}
如上面的代码,具体内容我们已经在Feign源码解析之生成jdk动态代理进行分析过。 有以下几种方式可以对feign的属性进行覆盖。
- EnableFeignClients#defaultConfiguration属性和FeignClient#configuration属性
- EnableFeignClients#defaultConfiguration对应的是全局属性的修改
- FeignClient#configuration对应单个feignClinet的属性的修改。
- 定义配置类将自定义的feign属性注入IOC容器
- 对应的是全局属性的修改。
- 如果用户没有进行自定义属性的注入,在FeignClientsConfiguration会有默认值的注入。
- 配置文件
-
可以修改的属性可以详见FeignClientConfiguration类的属性。
-
可以通过feign.client.config.default.[属性名]修改默认的全局属性,也可以通过feign.client.config.[clientName].[属性名]修改对应的feignClient的属性。
-
[clientName]的单个feignClient配置的优先级高于default的全局配置。
总结:
-上述3种方式修改的优先级为:2 < 1 < 3
- 如果增加配置项feign.client.defaultToProperties并设置为false,则优先级为 3 < 2 < 1。
需要注意的是:
- 1和2两种方式对应的都是application.getBean方法,通过前面的文章我们已经知道,没有FeignClient对应一个applicationContext,并且设置整个项目的applicationContext作为parent applicationContext。
- 在调用getBean方法获取对象时,会先从当前的applicationContext中进行查找,如果没有找到,再从parent applicationContext中进行查找,这也是为什么方式1的优先级高于方式2的原因。
- 因此,我们需要注意,不能通过方式1的EnableFeignClients#defaultConfiguration和FeignClient#configuration对相同的1个feign属性进行重复赋值,RequestInterceptor除外。
- 如果用户通过这两个属性对1个feign属性进行了两次注入,由于两者都是通过FeignClientSpecification类进行注入的,处于同一级的applicationContext中,而且BeanDefinition类的autowireCandidate、primary等属性都一致,系统无法判断成该采用哪个bean对象返回,会抛出NoUniqueBeanDefinitionException异常。
- 方式2也同理,不能针对1个feign属性往IOC容器注入两次,RequestInterceptor除外。
- 通过方式1的EnableFeignClients#defaultConfiguration和FeignClient#configuration不要通过@configuration,@component等方式注入IOC容器,否则会和方式2没有区别,变成全局配置。
二. RequestInterceptor
RequestInterceptor也是上文说的feign中属性的一种,是对feign方法的拦截器,在SynchronousMthodHandler类里转发请求前,会先进入RequestInterceptor进行处理。
Request targetRequest(RequestTemplate template) {
for (RequestInterceptor interceptor : requestInterceptors) {
interceptor.apply(template);
}
return target.apply(new RequestTemplate(template));
}
我们可以自定义RequestInterceptor的实现类对Feign请求增加公共操作,如公共的请求头数据等等。
在我们的项目里,会针对请求头的token进行鉴权,获取到登录人信息然后放到线程本地变量ThreadLocal中,但是一旦经过feign转发后,另一个模块无法进行获取,因此我们需要增加1个RequesInterceptor,获取到ThreadLocal值后按照一定的规则加入到请求头中。
不过,需要注意的是当feign中启用了hystrix,默认通过线程池隔离的方式会另起一个线程处理,此时ThreadLocal同样无法获取到。具体的解决方法有不少相关资料,可以参考Hystrix实现ThreadLocal上下文的传递了解。
三. AnnotatedParameterProcessor接口
AnnotatedParameterProcessor用来处理参数注解,springboot中默认的AnnotatedParameterProcessor的实现类有PathVariableParameterProcessor、RequestParamParameterProcessor、RequestHeaderParameterProcessor用来处理@PathVariable、@RequestParam、@RequstHeader。
用户可以自定义一些feign方法参数的注解,并自定义相关的AnnotatedParameterProcessor实现类将其映射到MethodMetaData中,方法参数的类型对应AnnotatedParameterProcessor的ANNOTATION属性。详细内容可以查看SpringMvcContract类的protected boolean processAnnotationsOnParameter(MethodMetadata data, Annotation[] annotations, int paramIndex)方法。
需要注意,用户一旦自定义AnnotatedParameterProcessor实现类并注入IOC容器,默认的3个AnnotatedParameterProcessor类将失效。如下面的代码所示,当新建并初始化SpringMvcContract时,只有传入的annotatedParameterProcessors参数是空的list时,才会调用getDefaultAnnotatedArgumentsProcessors方法获取默认的3个AnnotatedParameterProcessor类。而SpringMvcContract类在FeignClientsConfiguration配置类中被初始化,annotatedParameterProcessors参数对应的正是注入IOC容器的AnnotatedParameterProcessor实现类。
public SpringMvcContract(
List<AnnotatedParameterProcessor> annotatedParameterProcessors,
ConversionService conversionService) {
Assert.notNull(annotatedParameterProcessors,
"Parameter processors can not be null.");
Assert.notNull(conversionService, "ConversionService can not be null.");
List<AnnotatedParameterProcessor> processors;
if (!annotatedParameterProcessors.isEmpty()) {
processors = new ArrayList<>(annotatedParameterProcessors);
}
else {
processors = getDefaultAnnotatedArgumentsProcessors();
}
this.annotatedArgumentProcessors = toAnnotatedArgumentProcessorMap(processors);
this.conversionService = conversionService;
this.expander = new ConvertingExpander(conversionService);
}
private List<AnnotatedParameterProcessor> getDefaultAnnotatedArgumentsProcessors() {
List<AnnotatedParameterProcessor> annotatedArgumentResolvers = new ArrayList<>();
annotatedArgumentResolvers.add(new PathVariableParameterProcessor());
annotatedArgumentResolvers.add(new RequestParamParameterProcessor());
annotatedArgumentResolvers.add(new RequestHeaderParameterProcessor());
return annotatedArgumentResolvers;
}
如果feign方法的参数没有被AnnotatedParameterProcessor进行过解析,而且不是URI类,sprpingboot默认会按照RequestBody注解处理成请求的body参数,一个方法中最多只能有1个body参数。该限制在BaseContract的protected MethodMetadata parseAndValidateMetadata(Class<?> targetType, Method method)方法中进行校验。
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
boolean isHttpAnnotation = false;
if (parameterAnnotations[i] != null) {
isHttpAnnotation = processAnnotationsOnParameter(data, parameterAnnotations[i], i);
}
if (parameterTypes[i] == URI.class) {
data.urlIndex(i);
} else if (!isHttpAnnotation) {
checkState(data.formParams().isEmpty(),
"Body parameters cannot be used with form parameters.");
checkState(data.bodyIndex() == null, "Method has too many Body parameters: %s", method);
data.bodyIndex(i);
data.bodyType(Types.resolve(targetType, targetType, genericParameterTypes[i]));
}
}
四. 其它注意点
1. Feign接口不能是泛型接口,最多只能有1个且1层父接口。
- 即Feign接口不能是泛型接口,最多只能有1个父接口,并且这个父接口不能再有父接口。
- 在Feign源码解析之代理类的处理逻辑对SpringMvcContract的解析过程中,我们已经提到了这一点,在BaseContract类的public List
parseAndValidatateMetadata(Class<?> targetType)中对此进行了校验。
checkState(targetType.getTypeParameters().length == 0,
"Parameterized types unsupported: %s",
targetType.getSimpleName());
checkState(targetType.getInterfaces().length <= 1,
"Only single inheritance supported: %s",
targetType.getSimpleName());
if (targetType.getInterfaces().length == 1) {
checkState(targetType.getInterfaces()[0].getInterfaces().length == 0,
"Only single-level inheritance supported: %s",
targetType.getSimpleName());
}
2. 写在Feign接口的父接口里的方法同样有效
- 写在Feign接口的父接口里的方法同样会在jdk动态代理里被增强处理,能够映射成HTTP请求。
- 因此springboot在BaseContract类的public List
parseAndValidatateMetadata(Class<?> targetType)方法遍历Feign接口的方法时,使用的是getMethods。
for (Method method : targetType.getMethods()) {
if (method.getDeclaringClass() == Object.class ||
(method.getModifiers() & Modifier.STATIC) != 0 ||
Util.isDefault(method)) {
continue;
}
MethodMetadata metadata = parseAndValidateMetadata(targetType, method);
checkState(!result.containsKey(metadata.configKey()), "Overrides unsupported: %s",
metadata.configKey());
result.put(metadata.configKey(), metadata);
}
3. RequestMapping注解的value属性只有使用在Feign接口的最上面一层接口才具有前缀作用。
- 即当Feign接口没有父接口时,RequestMapping注解的value属性作为该接口内所有方法的url前缀;
- 当Feign接口有父接口时,Feign接口上的 RequestMapping注解的value属性将失效,此时父接口上的RequestMapping注解的value属性作为该接口内所有方法的url前缀。
- 这一点在Feign源码解析之代理类的处理逻辑中也有提到,在BaseContract类的
protected MethodMetadata parseAndValidateMetadata(Class<?> targetType, Method method)方法中。
if(targetType.getInterfaces().length == 1) {
processAnnotationOnClass(data, targetType.getInterfaces()[0]);
}
processAnnotationOnClass(data, targetType);
在SpringMvcContract的protected abstract void processAnnotationOnClass(MethodMetadata data, Class<?> clz);进行了判断,当clz.getInterfaces().length == 0才会进行处理。
@Override
protected void processAnnotationOnClass(MethodMetadata data, Class<?> clz) {
if (clz.getInterfaces().length == 0) {
RequestMapping classAnnotation = findMergedAnnotation(clz,
RequestMapping.class);
if (classAnnotation != null) {
// Prepend path from class annotation if specified
if (classAnnotation.value().length > 0) {
String pathValue = emptyToNull(classAnnotation.value()[0]);
pathValue = resolve(pathValue);
if (!pathValue.startsWith("/")) {
pathValue = "/" + pathValue;
}
data.template().insert(0, pathValue);
}
}
}
}
4. 对于RequestMapping注解的produces、consumers、headers属性,Feign接口和父接口上的RequestMapping注解都有效,且Feign接口的RequestMapping注解会覆盖父接口上的注解。
- 即当Feign方法上的RequestMapping注解没有设置produces、consumers、headers属性时,会读取Feign接口上的RequestMapping注解的对应属性进行配置,即使接口的RequestMapping注解也没有配置这些属性。
- 如果Feign接口没有RequestMapping注解时,才轮到其父接口上的RequestMapping注解发挥效果。
- 这一点在Feign源码解析之代理类的处理逻辑中也有提到,在BaseContract类的public MethodMetadata parseAndValidateMetadata(Class<?> targetType, Method method)方法中。
@Override
public MethodMetadata parseAndValidateMetadata(Class<?> targetType, Method method) {
this.processedMethods.put(Feign.configKey(targetType, method), method);
MethodMetadata md = super.parseAndValidateMetadata(targetType, method);
RequestMapping classAnnotation = findMergedAnnotation(targetType,
RequestMapping.class);
if (classAnnotation != null) {
// produces - use from class annotation only if method has not specified this
if (!md.template().headers().containsKey(ACCEPT)) {
parseProduces(md, method, classAnnotation);
}
// consumes -- use from class annotation only if method has not specified this
if (!md.template().headers().containsKey(CONTENT_TYPE)) {
parseConsumes(md, method, classAnnotation);
}
// headers -- class annotation is inherited to methods, always write these if
// present
parseHeaders(md, method, classAnnotation);
}
return md;
}
综合一下2、3、4,举一个例子。有Feign接口如下:
@FeignClient(value = "shop")
@RequestMapping(value = "/shops2", produces = "application/xml")
public interface ShopFeignClient extends BaseFeignClient {
}
其父接口如下:
@RequestMapping(value = "/shops", produces = "text/html", consumes = "application/json")
public interface BaseFeignClient {
@GettMapping("/{shopId}")
Shop getShopById(@PathVariable("shopId") Long shopId);
}
最后在SynchronousMethodHandler中的RequestTemplate的值如下图:
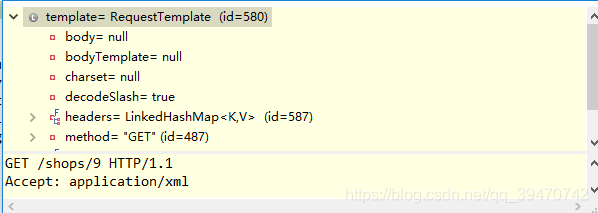
定义多个指向同一个服务的FeignClient需要保证bean alias不同且configuration属性相同。虽然理论上可以创建多个指向同一个服务的FeignClient,因为指向同一个服务说明FeignClient的name相同,那么需要注意一下两点:
- bean的别名alias:FeignClient注解的接口注入后的bean的alias默认为name + “.FeignClient”,因此如果有多个name相同的FeignClient,需要通过设置FeignClient的qualifier属性来保证alias的不同。
- FeignClient的configuration属性:在FeignContext中configurations是由一个map结果,key值为name,value为EnbaleFeignClient个FeignClient的configuration属性,根据configurations生成的contexts也是以name为key值。因此,需要保证多个指向同一个服务的FeignClient的configuration属性应该保持一致,否则springboot无法进行区分。因此,不建议定义多个指向同一个服务的FeignClient,如果真的需要这么做,务必保证bean alias不同且configuration属性相同。
本文由 创作,采用 知识共享署名4.0 国际许可协议进行许可。本站文章除注明转载/出处外,均为本站原创或翻译,转载前请务必署名。最后编辑时间为: 2021/07/30 02:23
